Are you driving a 2006 Honda Civic and noticing peculiar electrical issues? If so, it could be a sign of a malfunctioning DC-DC converter—a critical component for your vehicle’s electrical system, particularly in hybrid models. In a world where we depend more on our gadgets than ever, the last thing you want is to face unexpected car troubles, especially when they stem from an unseen issue like the DC-DC converter. Here’s a comprehensive guide to diagnosing a bad DC-DC converter, arming you with the knowledge to keep your ride smooth and efficient.
The DC-DC converter plays a pivotal role in transforming high-voltage energy from the hybrid battery into the lower voltage needed for your car’s 12V electrical system. When this converter falters, it can lead to a cascade of issues, from weak headlights to battery drain. Therefore, comprehending the signs of a failing converter is crucial for young drivers and car enthusiasts alike. Here’s how you can get started on your diagnostic journey.
Recognizing the Symptoms
If your Civic’s electrical system has begun to exhibit some peculiar behaviors, keep an eye out for these common symptoms that may indicate a failing DC-DC converter:
- Dim or Flickering Lights: Have you noticed your headlights flickering or dimming while driving? This third-rate lighting can signify that the DC-DC converter is woefully inadequate.
- Frequent Battery Issues: If you find yourself jumping your battery more often than you’d like, take note. A dysfunctional DC-DC converter can drain the 12V battery prematurely.
- Faulty Electronics: Experiencing issues with your music system, power windows, or dashboard lights? These electronic malfunctions might stem from a lack of sufficient power being provided by the converter.
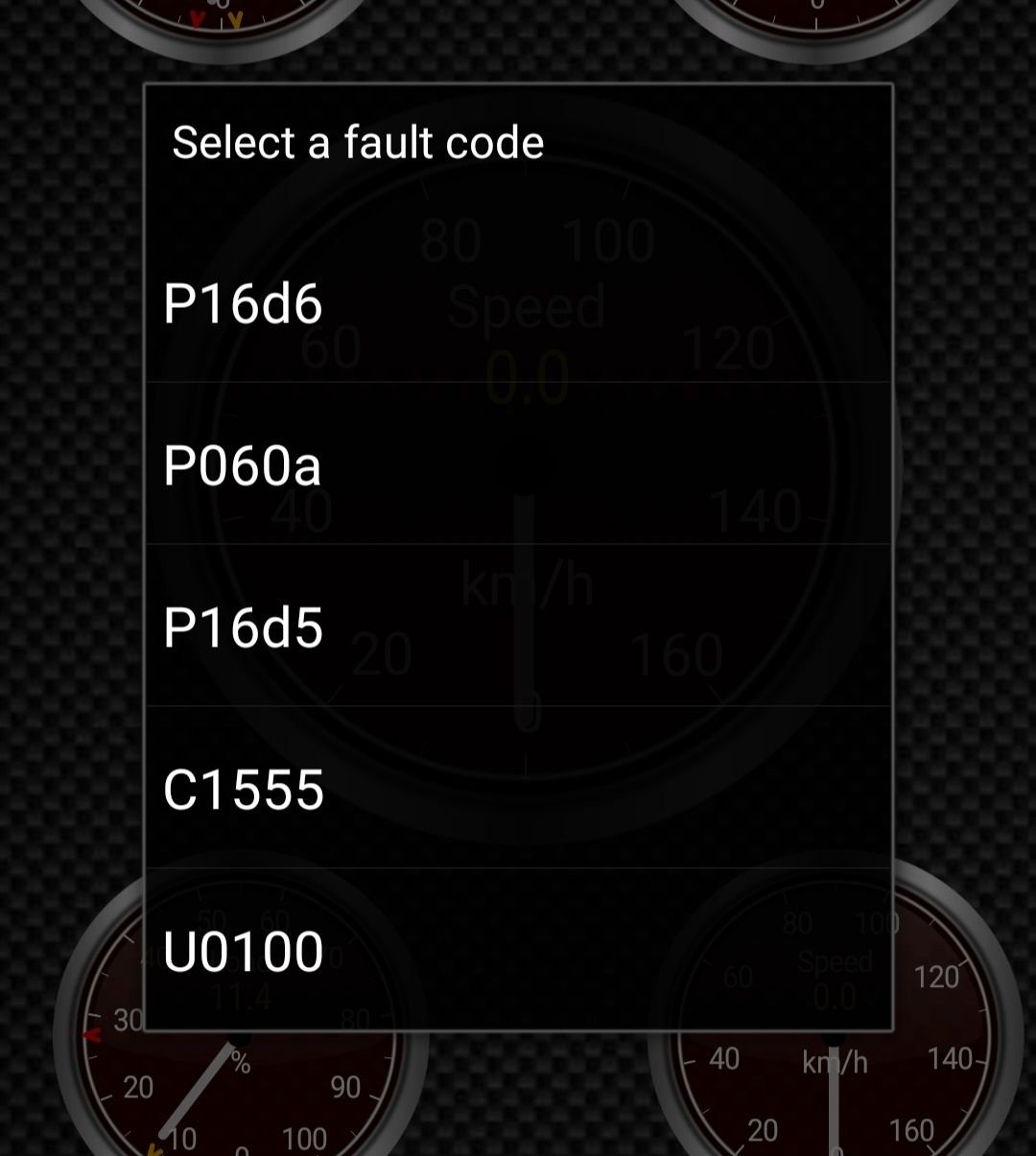
- Error Codes: If the check engine light illuminates, it might represent an underlying issue with the converter. Utilize an OBD-II scanner to retrieve any diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs).
The Preliminary Steps
Before delving deeper into diagnostic methods, it’s advisable to perform some initial inspections. This can save you time and trouble:
- Visual Inspection: First and foremost, pop the hood and take a gander at the DC-DC converter itself, typically located near the hybrid battery. Look for signs of physical damage, burnt connections, or corrosion.
- Battery Condition: Assess the state of the 12-volt battery. A fully charged battery that shows signs of weakness might indicate that the converter is not transferring enough power.
- Connector Examination: Ensure that all connectors are secure and free from rust or environmental factors that could impede electrical flow.
Utilizing Diagnostic Tools
If your cursory checks yielded no red flags, it’s time to grab some tools to aid in your diagnosis. Here’s how to step it up:
- Multimeter Testing: Utilizing a multimeter is essential for measuring voltage. First, check the output voltage of the DC-DC converter. You should see approximately 13.5 to 14.5 volts when the hybrid system is operating. A significantly lower reading could signal converter failure.
- Voltage Drop Test: Perform a voltage drop test on the battery cables and connections. Inadequate voltage readings here can lead back to the DC-DC converter, indicating resistance in the electrical pathway.
- Load Test: If the converter seems functional, try performing a battery load test. This checks if the battery can sustain normal use when under strain. A weak battery could complicate your diagnosis.
Deeper Computer Diagnostics
If all else fails, a visit to a professional shop equipped with advanced computer diagnostic tools may be indispensable. Technicians can evaluate error codes more thoroughly and even check the vehicle’s battery management system. However, if you wish to handle it yourself:
- Scan for Codes: Using an OBD-II scanner, look for specific fault codes that may indicate converter issues. Codes such as P0A0F could signify faults in the hybrid battery or DC-DC converter.
- Hybrid Battery Management System Check: Review the health of the hybrid battery and the BMS. If either shows irregularities, the issue may not originate solely from the DC-DC converter.
Conclusion: Know When to Seek Help
Diagnosing a bad DC-DC converter in your 2006 Honda Civic may seem daunting, especially if you’re a younger driver new to the intricacies of vehicle maintenance. However, with methodical steps and proper equipment, you can redefine your understanding of your car’s electrical ecosystem. Not only will it save you time and money in the long run, but it also empowers you to address issues that arise with confidence. Should challenges persist—even after thorough diagnostics—consider enlisting the expertise of a certified technician. Keeping your Civic in optimal condition ensures that it continues to be an efficient partner on the road for years to come.