When it comes to elevating security at your premises, nothing beats the efficacy of a magnetic door lock. As the modern world progresses, the need for enhanced access control systems becomes paramount. Picture this: a mood-boosting experience wherein you feel completely secure in your personal space; magnetic door locks facilitate just that. These advanced locking mechanisms not only offer unbeatable safety but also contribute to an aura of sophistication and peace of mind. Navigating the complexities of magnetic door lock wiring can seem daunting at first, but by demystifying the process, you can empower yourself to take control of your security needs.
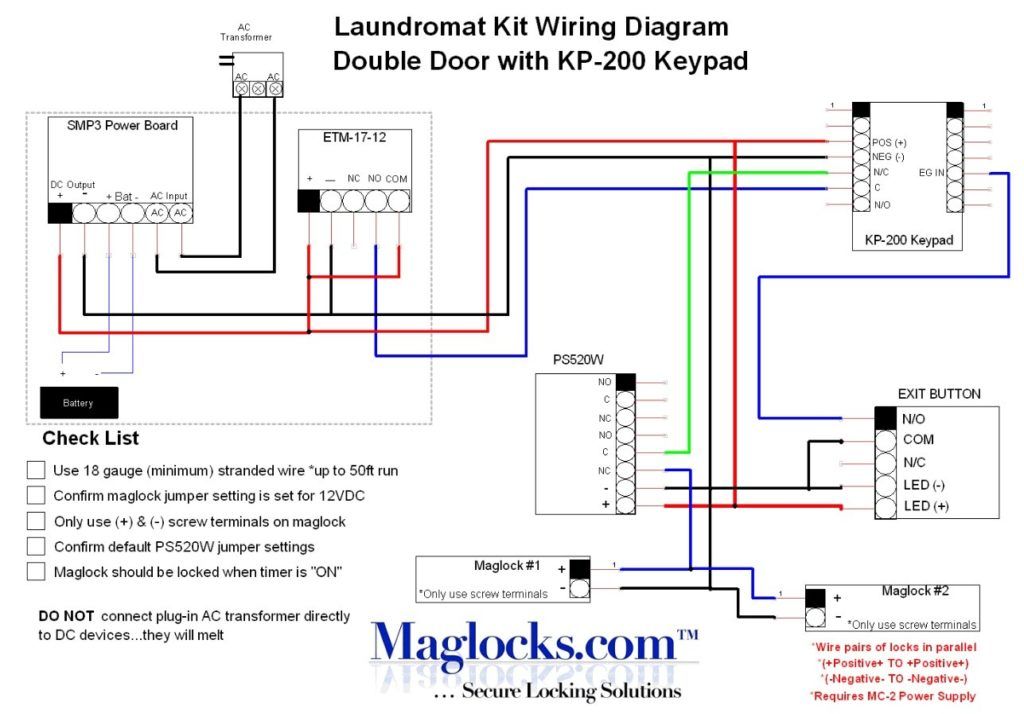
Magnetic door locks, also known as electromagnetic locks (or maglocks), employ the principles of electromagnetism to provide exceptional security. These locks are generally comprised of two main components: an electromagnet and an armature plate. When power is supplied to the electromagnet, it generates a magnetic field, effectively binding the armature plate to the magnet. When the power supply is cut, the magnetic field dissipates, allowing the door to open freely. Simple in concept but elegant in function, understanding the wiring involved in setting up these devices is essential to ensure optimal performance.
Delving into the wiring of magnetic door locks begins with understanding the two primary types of wiring configurations: normally closed (NC) and normally open (NO). In a normally closed configuration, the circuit is complete when the magnetic lock is energized, thus locking the door. Conversely, in a normally open configuration, the circuit remains open until power is supplied, at which point the door locks. Your choice between these configurations ultimately hinges on the desired operation of your access control system. For example, a normally closed configuration is commonly used in environments where security is of utmost importance, as it prevents unauthorized access at all times.
Another critical consideration is the power supply. Most magnetic locks operate on a 12V to 24V DC power source. The choice of voltage impacts not only the power consumption but also the unlocking speed. Higher voltages tend to provide faster unlocking responses, making them ideal for high-traffic areas. However, it is crucial to ensure that your power supply is reliable and equipped with an appropriate power backup system. An unforeseen power failure could render the magnetic lock ineffective, compromising your security. In conjunction, consider the application of a surge protector to guard against voltage spikes that could potentially damage the lock mechanism.
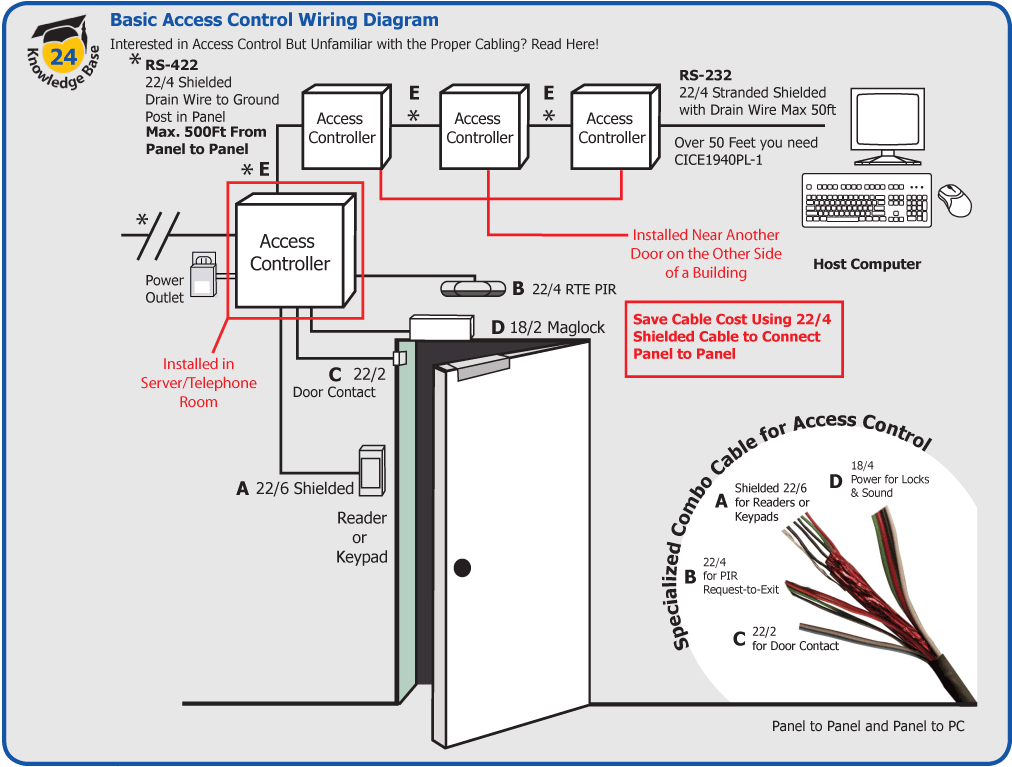
Wiring a magnetic door lock generally involves three fundamental connections: the positive power supply, the negative power supply, and the connecting wires to the access control system. Careful attention should be paid to the color coding of wires—typically red represents positive, black signifies negative, and additional wires may be employed for signaling purposes. To secure a solid connection, utilize connectors or terminal blocks compatible with the wire gauge being employed. Failing to ensure reliable connections can lead to intermittent locking issues, which can compromise the overall effectiveness of your system.
Integrating the magnetic lock with an access control system further enhances its capabilities. This can be accomplished through keypads, card readers, or biometric scanners. Each type of access control mechanism offers unique advantages. For instance, keypads require users to input a PIN for entry, while card readers offer the convenience of swiping a card. On the most advanced end, biometric scanners utilize unique physiological traits—like fingerprints or facial recognition—to grant access. In most cases, these systems require additional wiring to connect to the magnetic door lock, culminating in a more comprehensive approach to security.
To ensure seamless operation, it is prudent to establish a fail-safe or fail-secure mechanism. A fail-safe system unlocks the door in the event of a power failure, thereby providing safety to occupants. This is especially important in scenarios where emergency egress is vital, such as in office buildings or hospitals. Conversely, a fail-secure system maintains the locked status during a power loss, thereby protecting valuable assets but potentially risking occupant safety. Each choice entails weighing the risks and benefits and aligning the decision with your specific security needs.
It’s advisable to consult with a qualified professional for the installation of a magnetic door locking system; however, a DIY enthusiast may also equip themselves with the proper tools and guidance. High-quality installation ensures that the lock is not only secure but also functioning as intended. Furthermore, conducting periodic maintenance checks will ensure the longevity and reliability of the magnetic door lock. Examine connections, inspect for frayed wires, and test the operation of the locking mechanism to ensure continued peace of mind.
In conclusion, the world of magnetic door lock wiring presents opportunities for bolstering security in your personal or professional spaces. Understanding the fundamental components, wiring configurations, and integration with access control systems empowers you to create an environment that not only deters potential intruders but also enhances your mood by offering a sanctuary of safety. With increasing advancements in technology, the future promises to deliver even more sophisticated solutions. As you embark on your journey of securing your space with magnetic locks, remember that knowledge is the first step towards achieving a mood-boosting, secure environment.