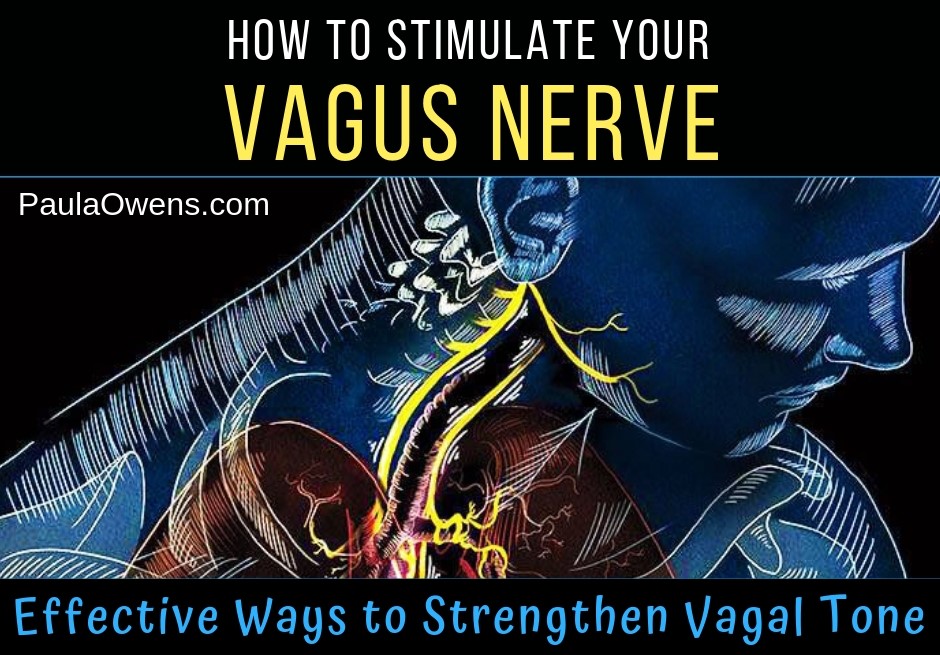
Imagine the serene presence of Yoda from Star Wars, his calm demeanor balancing the chaos around him. Or think of Simba from The Lion King, who gradually learns to navigate life’s trials by listening to his instincts. Amidst the nuances of pregnancy, such tranquil resilience can stem from an often-overlooked yet immensely significant component of human physiology: the vagus nerve. This intricate cranial structure plays a pivotal role in modulating our body’s responses, particularly during the transformative journey of pregnancy. The influence of vagal tone—indicative of the vagus nerve’s activity—on maternal health is indeed a fascinating subject.
The vagus nerve is one of the twelve cranial nerves and governs a plethora of autonomic functions, including heart rate and digestion. While it may seem obscure, its impact is profound, especially in the context of maternal well-being. Understanding vagal tone unveils a nuanced insight into both physical and emotional health during pregnancy, making it a vital subject for expectant mothers and healthcare providers alike.
In medical parlance, **vagal tone** refers to the degree of activity of the vagus nerve, measured primarily through heart rate variability (HRV). A higher vagal tone denotes a robust parasympathetic nervous system, characterized by a relaxed state, adept emotional regulation, and enhanced resilience to stress. For expectant mothers, maintaining a healthy vagal tone can have a range of implications that intertwine closely with both maternal and fetal health.
Pregnancy introduces a multitude of physiological changes that can induce stress and anxiety. Fluctuating hormones, rapid bodily changes, and the impending responsibilities of motherhood can engender a cataclysmic swirl of emotions. This is where the vagus nerve comes into play. A well-toned vagus nerve allows pregnant individuals to better handle stress through its influence on heart rate and emotional responses. With higher vagal tone, a mother can achieve a more balanced emotional state, which is critical for her wellbeing and, by extension, her developing child.
Research indicates that elevated vagal tone is linked to positive maternal outcomes. The benefits extend beyond emotional stability; physiological adaptations such as enhanced digestion and improved circulation can be observed. For instance, when the vagus nerve is operating efficiently, it supports nutrient absorption and optimizes fetal growth and development. Moreover, a pregnant woman with a high vagal tone may experience fewer complications, such as gestational diabetes and hypertension, which can jeopardize both her health and her baby’s.
Drawing from psychological perspectives, maternal stress can have devastating consequences on fetal development, potentially resulting in lasting imprints on the offspring’s health. Such stress maladaptations can culminate in cognitive and emotional challenges in later life. However, by nurturing a high vagal tone through integrative practices like mindfulness, yoga, and deep breathing exercises—much like Yoda’s contemplative practices—mothers can cultivate emotional resilience. Such methods have demonstrated promising results in promoting vagal activity and, subsequently, maternal wellbeing.
In addition to emotional regulation, the vagus nerve plays a crucial role in fostering a connection between the mother and her unborn child. This communication channel is facilitated through hormonal signalling and nerve pathways that connect to both the heart and gut. Engaging in vagal-stimulating activities can thus serve a dual purpose: enhancing maternal health while simultaneously providing a calm, nurturing environment for the fetus. Activities such as gentle swimming or prenatal massages can evoke a soothing cascade of benefits, making them essential components of a holistic prenatal regimen.
Furthermore, studies illustrate that vagal tone can also affect birthing experiences. A mother with a well-toned vagus nerve tends to experience lower anxiety during labor, leading to improved overall satisfaction with the birthing process. This serene state can contribute to the progress of labor, as oxytocin—a hormone critical for childbirth—requires a sense of calm to function optimally. As a result, enhancing vagal tone can pave the way for a more positive and empowering birthing experience.
Despite the intrinsic benefits linked to improved vagal tone, many expectant mothers encounter challenges. Societal pressures, work stress, and even the digital distractions of modern life can hinder the body’s parasympathetic responses. Hence, fostering a greater awareness of vagal health becomes imperative. Incorporating practices that promote relaxation and mindfulness should be viewed not merely as “extras” during pregnancy; they are foundational to both maternal and fetal health.
In conclusion, the vagus nerve’s influence during pregnancy is nothing short of transformative. By understanding and enhancing vagal tone, expectant mothers can achieve a sense of equilibrium that permeates both their physical and emotional landscapes. Just as Simba learns to trust his instincts, mothers can learn to trust the profound biological wisdom at play and embrace practices that bolster their vagal health. In this intricate dance of motherhood, where both mother and child thrive, the vagus nerve stands as a silent yet influential guide, crucial for nurturing a healthy transition into the vibrant world of motherhood.