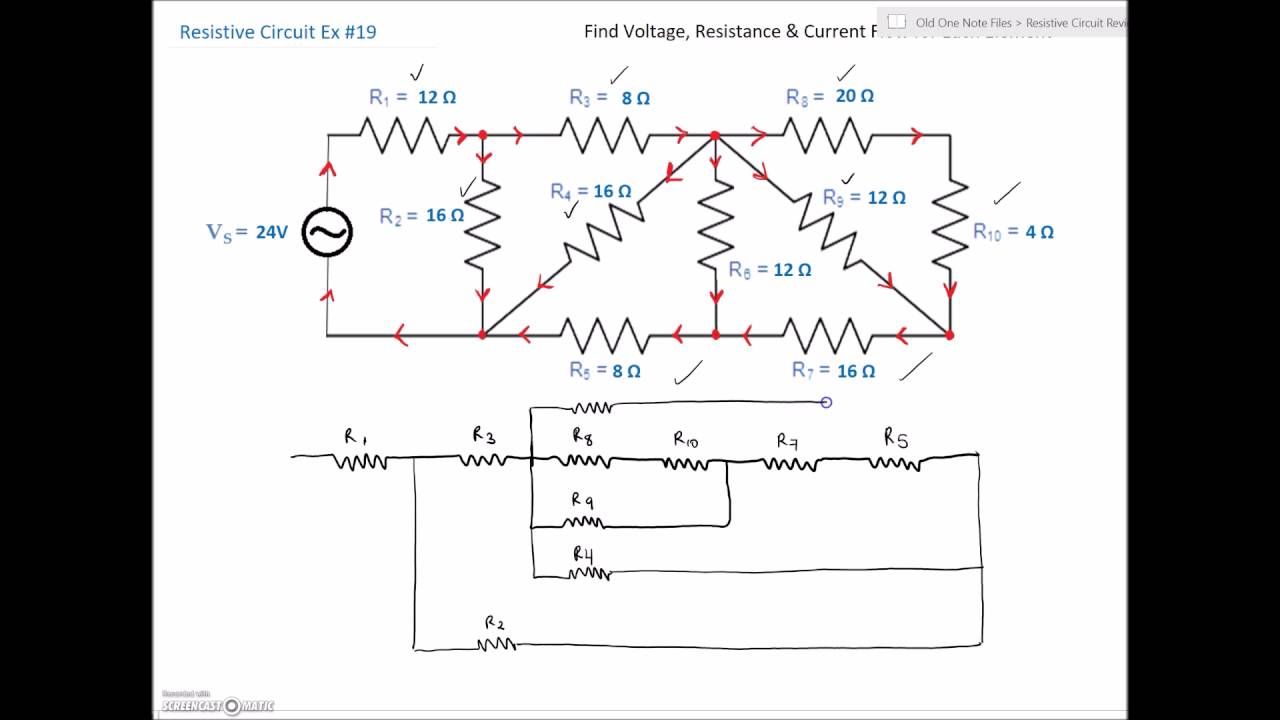
Have you ever felt overwhelmed by the intricacies of electrical circuits? The confusion often stems from the combination of series and parallel components, rendering what should be a straightforward task into a perplexing ordeal. Understanding series-parallel circuits is essential not only for budding engineers but also for hobbyists attempting to tackle their DIY projects. This article aims to decode the complexities of such circuits and provide you with a systematic approach to solving them, making the seemingly insurmountable challenges much more manageable.
At the crux of electrical engineering lies the fascinating world of circuits, where components interact to create predictable outcomes. Series circuits consist of components connected end-to-end, where the current flows through each element sequentially. In contrast, parallel circuits offer multiple pathways, allowing current to traverse through various branches simultaneously. The beauty of series-parallel circuits emerges when these two configurations intertwine, resulting in an elegant yet complex system that requires careful analysis.
The first step in mastering series-parallel circuits is to dissect the configuration and understand the behavior of each component involved. Begin by identifying whether the circuit is predominantly series, predominantly parallel, or a hybrid of both. This classification will dictate how you approach the analysis. Remember, in a series circuit, the total resistance is the sum of individual resistances, while in a parallel circuit, the total resistance is determined using the reciprocal sum of each resistance. The following equations eloquently articulate this distinction:
- Series Resistance: Rtotal = R1 + R2 + R3 + … + Rn
- Parallel Resistance: 1/Rtotal = 1/R1 + 1/R2 + 1/R3 + … + 1/Rn
With a firm grasp of resistance calculations in your toolkit, it is prudent to employ a stepwise approach when solving complex circuits. Begin by simplifying the circuit incrementally. Focus on isolated sections that can be treated as independent series or parallel networks. Once you calculate the total resistance for these segments, reintegrate them into the larger circuit framework, and repeat the process. This reduction method allows you to avoid the labyrinth of calculations that often leads to miscalculations and frustration.
In scenarios where voltage and current are key focal points, Ohm’s law becomes an invaluable ally. By relating voltage (V), current (I), and resistance (R) through the formula V = I × R, you can unravel the dependencies within the circuit. This formula is particularly handy when determining how voltage divides in series circuits and how it remains the same across parallel branches.
Furthermore, understanding Kirchoff’s laws is pivotal for those delving deeper into complex circuit analysis. Kirchoff’s Voltage Law (KVL) asserts that the total sum of electrical potential differences around a closed loop must equal zero. Conversely, Kirchoff’s Current Law (KCL) states that the total current entering a junction must equal the total current leaving it. Mastery of these foundational principles empowers circuit solvers to navigate through intricate scenarios with confidence.
As you delve further into the realm of series-parallel circuits, you may encounter components such as capacitors and inductors. These reactive components behave distinctly in circuits, introducing additional layers of complexity. Capacitors store energy in an electric field, affecting how voltage is distributed, while inductors store energy in a magnetic field, influencing current flow. Their placement in a circuit can dramatically alter its overall behavior, so it’s crucial to apply the same analytical techniques that you would reserve for resistive networks.
Technology has paved the way for various circuit simulation tools that can expedite the problem-solving process for series-parallel circuits. Software applications like LTspice and Multisim allow users to create virtual models of their circuits, providing immediate feedback on expected behavior. These digital tools not only aid in verifying calculations but also serve as excellent educational resources for those seeking a hands-on understanding of circuit dynamics.
However, despite technological advancements, there remains an intrinsic value in mastering manual calculations. This proficiency equips you with a fundamental understanding of how circuits operate and deepens your analytical skills. When confronted with a malfunctioning circuit or an unexpected outcome, having a solid foundation will allow you to troubleshoot effectively and efficiently.
In conclusion, the world of series-parallel circuits does not have to be a daunting enigma. Embrace the systematic approach of breaking down complex configurations into manageable components. Leverage Ohm’s law, Kirchoff’s rules, and simulation tools to navigate through the intricacies. With practice and patience, you will find yourself unraveling the mysteries of electrical circuits with newfound ease, transforming challenges into triumphs. By honing your skills, you not only enhance your understanding but also empower yourself to innovate and create in a field brimming with potential.