Understanding electrical systems requires a comprehension of various components, and transformers play a crucial role in managing voltage levels. Among these, the step-down transformer is vital for reducing voltage from high to low levels, making it safe for use in residential and commercial settings. The discussion surrounding step-down transformers often centers on their efficiency and application, yet a more nuanced perspective reveals the intricacies of their wiring and operational characteristics. This guide seeks to explore everything you need to know about step-down transformer wiring and its significance in electrical engineering.
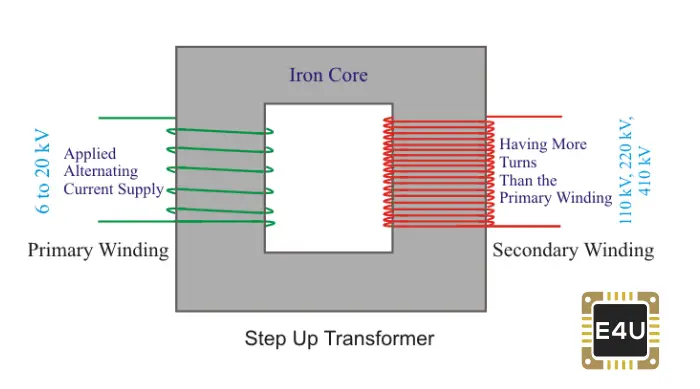
To begin, let’s delve into the fundamental principles of a step-down transformer. A transformer operates under the law of electromagnetic induction, converting electrical energy from one voltage level to another without changing the frequency of the current. A step-down transformer specifically reduces voltage through its turns ratio—the ratio of the number of windings in the primary coil to that in the secondary coil. This mechanism is pivotal in various applications, particularly in distributing electrical power effectively and safely.
The design of a step-down transformer comprises two main components: the primary winding and the secondary winding. The primary winding connects to the high-voltage source, while the secondary winding outputs the reduced voltage. To illustrate, consider a transformer with a turns ratio of 10:1. A primary voltage of 240V would yield a secondary voltage of just 24V, an essential characteristic in supplying lower voltage to devices that cannot handle the higher voltages prevalent in the main supply.
Now, let’s discuss the wiring specifics of a step-down transformer. Proper wiring is paramount for both functionality and safety. The wiring scheme includes various connections that must be meticulously followed. Typically, the primary side consists of insulated conductors that transport electricity from the source. The secondary side then transmits the lower voltage to designated loads. Using appropriate wire gauge is crucial, as insufficiently sized wires may result in overheating and ultimately lead to system failure.
In addition to the basic wiring requirements, grounding plays a significant role in transformer installations. A ground connection helps in dissipating any leakage currents, thereby enhancing safety. It is paramount that the grounding system is robust, as it protects both equipment and personnel from potential electrical faults. The National Electrical Code (NEC) provides extensive guidelines that should be adhered to during installation to ensure compliance with safety regulations.
Moreover, one must consider the physical layout during wiring. Avoiding congested areas and maintaining clear paths can mitigate interference from other electrical components and reduce the risk of accidental short circuits. Furthermore, it’s advisable to utilize conduit for protection, particularly in environments susceptible to physical damage. This not only safeguards the wiring but also enhances the aesthetic aspect of the installation.
When discussing the operation of step-down transformers, voltage regulation becomes an essential topic. While these transformers effectively reduce voltage, fluctuations in the input voltage can present challenges. Voltage regulation is a measure of how much the output voltage changes in response to variations in input voltage or load conditions. A well-designed step-down transformer can maintain steady output, ensuring that connected devices receive consistent power. This stability is crucial, particularly in sensitive applications such as audio and computer systems, where voltage irregularities can lead to malfunctions.
Additionally, maintenance of step-down transformers should not be overlooked. Regular inspection is suggested to identify signs of wear or damage. Common issues include insulation degradation, overheating, and signs of arcing. Timely maintenance and adherence to operational guidelines can alleviate potential hazards, extend the lifespan of the transformer, and ensure it operates at peak efficiency.
One cannot ignore the ecological aspect of transformers in modern applications. As focus shifts towards sustainable energy, efficient transformers contribute to reducing energy waste. Higher efficiency often translates to lower operational costs and a smaller carbon footprint, aligning with global trends toward energy conservation. Therefore, the selection of a quality step-down transformer that meets energy efficiency standards is not merely an economic decision but also an ethical one.
In conclusion, a comprehensive understanding of step-down transformer wiring encompasses both theoretical principles and practical considerations. By examining aspects such as wiring specifics, grounding practices, voltage regulation, maintenance, and ecological impacts, one can appreciate the significance of these components in the broader context of electrical systems. As technology progresses, the role of step-down transformers remains pivotal in adapting to the ever-evolving landscape of energy distribution and consumption. For those in the field, recognizing the depth of knowledge required will ultimately lead to safer and more efficient practices in electrical engineering.